
After P and G are generated, the carries for every bit position are created. In most cases, P is simply the sum output of a half adder and G is the carry output of the same adder. They work by creating two signals ( P and G) for each bit position, based on whether a carry is propagated through from a less significant bit position (at least one input is a 1), generated in that bit position (both inputs are 1), or killed in that bit position (both inputs are 0). To reduce the computation time, engineers devised faster ways to add two binary numbers by using carry-lookahead adders (CLA). Ī design with alternating carry polarities and optimized AND-OR-Invert gates can be about twice as fast. Assumed that an XOR gate takes 1 delays to complete, the delay imposed by the critical path of a full adder is equal to The critical path of a full adder runs through both XOR gates and ends at the sum bit s. The sum-output from the second half adder is the final sum output ( S) of the full adder and the output from the OR gate is the final carry output ( C out).
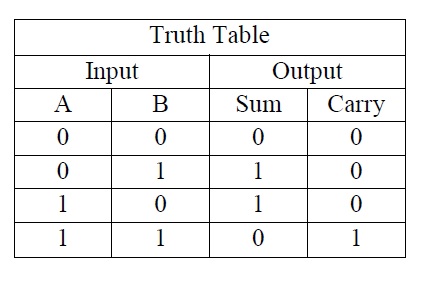
Using only two types of gates is convenient if the circuit is being implemented using simple integrated circuit chips which contain only one gate type per chip.Ī full adder can also be constructed from two half adders by connecting A and B to the input of one half adder, then taking its sum-output S as one of the inputs to the second half adder and C in as its other input, and finally the carry outputs from the two half-adders are connected to an OR gate. In this implementation, the final OR gate before the carry-out output may be replaced by an XOR gate without altering the resulting logic. One example implementation is with S = A ⊕ B ⊕ C in and C out = ( A ⋅ B) + ( C in ⋅ ( A ⊕ B)). Output carry and sum typically represented by the signals C out and S, where the sum equals 2 C out + S.Ī full adder can be implemented in many different ways such as with a custom transistor-level circuit or composed of other gates. The full adder is usually a component in a cascade of adders, which add 8, 16, 32, etc. A one-bit full-adder adds three one-bit numbers, often written as A, B, and C in A and B are the operands, and C in is a bit carried in from the previous less-significant stage. Full adder built up from nine NAND gates.Ī full adder adds binary numbers and accounts for values carried in as well as out.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
